在深度学习微调大模型时,LoRA(Low-Rank Adaptation) 提供了一种高效、轻量的微调方法。本文讲述了LoRA的原理,同时结合一个小型 MNIST 实验做了验证。
1. LoRA 的核心思路
在训练大模型时,通常模型参数量巨大,直接微调成本很高。LoRA 提出的想法很直观:不要修改原始权重,只在权重上加一个低秩增量。
假设我们有一个线性层:
LoRA 将权重分解为:
A 的维度 [r, in]B 的维度 out, rr << in, out- 推理时输出为:
这里的 α 是缩放因子,用来控制增量权重的数值大小。
核心优势就是:只训练低秩矩阵 B 和 A,原权重 W 保持冻结。显存和训练开销都低很多。
2. 小型实验:MNIST 新增特征微调
- Base 模型:普通小型 CNN,不带额外特征
- Feature 模型:输入额外亮度特征 + LoRA
- 微调流程:先训练 base,迁移权重到 feature 模型,只训练 LoRA 和新增特征
CNN模型
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
| class CNN(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, feature_dim=0):
super().__init__()
self.feature_dim = feature_dim
self.conv = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(1, 8, 3, padding=1),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.MaxPool2d(2),
nn.Conv2d(8, 16, 3, padding=1),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.MaxPool2d(2)
)
self.flatten_dim = 16 * 7 * 7
self.fc1 = nn.Linear(self.flatten_dim + feature_dim, 64)
self.fc2 = nn.Linear(64, 10)
def forward(self, x, feat=None):
x = self.conv(x)
x = x.view(x.size(0), -1)
if self.feature_dim > 0:
x = torch.cat([x, feat], dim=1)
x = F.relu(self.fc1(x))
x = self.fc2(x)
return x
|
feature_dim=0 → base CNNfeature_dim=1 → CNN + 额外亮度特征
额外亮度特征
1
2
3
| def extra_feature_brightness(img_batch):
feat = img_batch.mean(dim=[1, 2, 3], keepdim=True)
return feat.view(feat.size(0), -1)
|
LoRA 包装
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
| class LoRAWrapper(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, orig_linear, r=8, alpha=16, freeze_base=True):
super().__init__()
self.weight = nn.Parameter(orig_linear.weight.data.clone())
self.bias = nn.Parameter(orig_linear.bias.data.clone())
if freeze_base:
self.weight.requires_grad = False
self.bias.requires_grad = False
self.A = nn.Parameter(torch.randn(r, orig_linear.in_features) * 0.01)
self.B = nn.Parameter(torch.zeros(orig_linear.out_features, r))
self.scaling = alpha / r
def forward(self, x):
base = F.linear(x, self.weight, self.bias)
return base + self.scaling * ((x @ self.A.t()) @ self.B.t())
|
LoRA 对CNN模型中的全连接层 fc1 和 fc2 进行包裹,使得训练时仅更新增量矩阵。
迁移权重
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
| def load_base_into_feature_model(model_feat, base_state):
new_state = model_feat.state_dict()
for key in base_state:
if key not in new_state:
continue
old_w = base_state[key]
new_w = new_state[key]
if old_w.shape == new_w.shape:
new_state[key] = old_w.clone()
elif key == "fc1.weight":
new_state[key][:, :old_w.shape[1]] = old_w.clone()
else:
pass
model_feat.load_state_dict(new_state)
|
对于 fc1.weight 这种因新增额外特征而多出一列的层,只拷贝已有列,新增列保持随机初始化。
训练流程
- 训练 Base CNN → 保存权重
- 构建 Feature CNN + LoRA → 迁移 base 权重
- 微调 Feature CNN,仅训练 LoRA 参数 + 额外特征
- 记录训练/测试准确率
迁移 fc1 权重时注意:
- Base fc1:
[64, 784]
- Feature fc1:
[64, 784 + 1]
- 前 1568 列拷贝,最后一列随机初始化
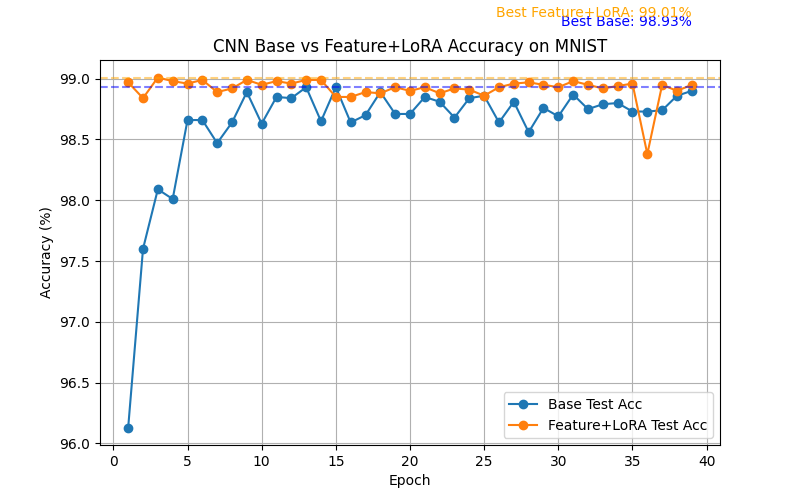
实验结果
- Base CNN 收敛到合理准确率
- Feature+LoRA 微调后,利用额外特征可以轻微提升